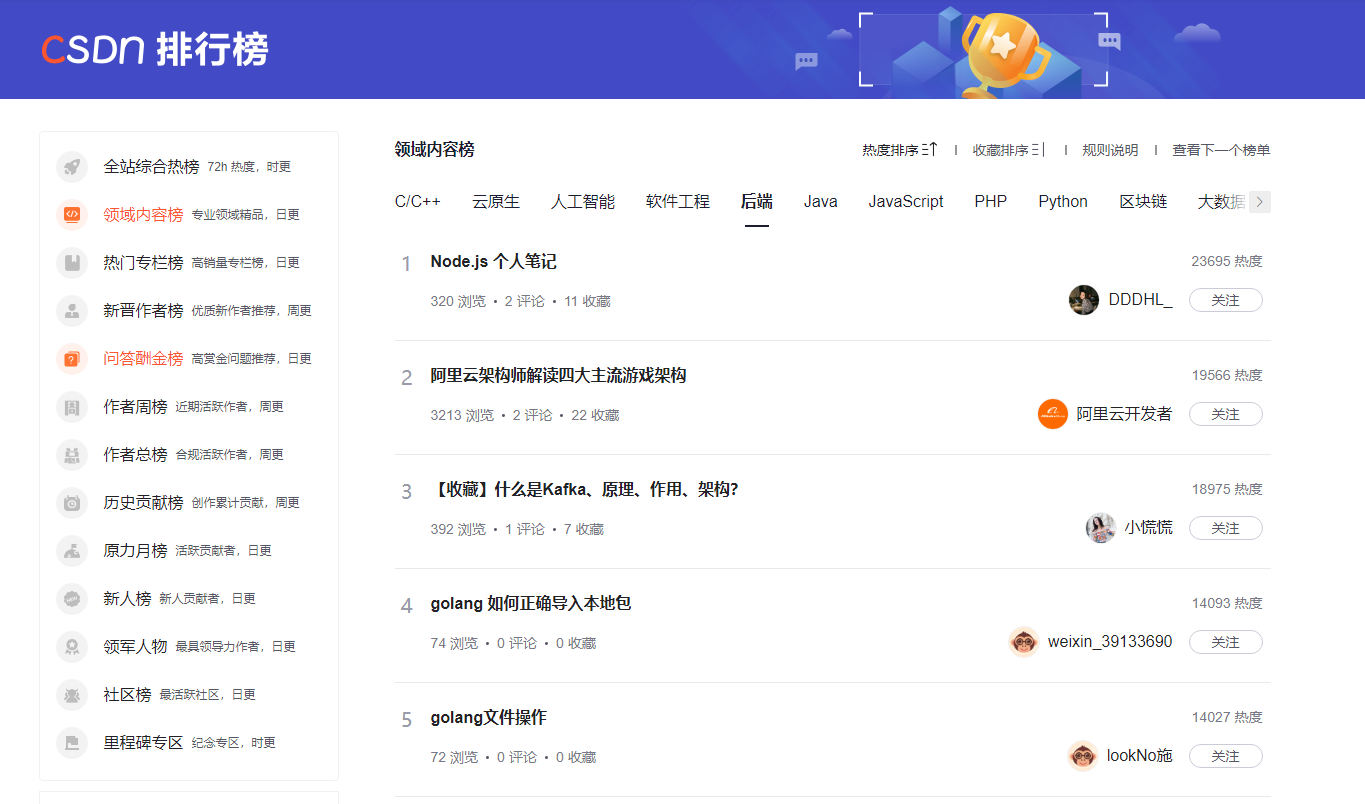
分享一下 node.js 学习笔记。已同步发布在 CSDN,获得排名太开心了!mark 一下~
# 一、fs 模块
引用
const fs = require('fs')
# 1.fs.readFile()
// options 代表编码格式读取
fs.readFile(path, [, options], callback)
2
// 示例 读取成功 err=null 读取失败 data=undefined
fs.readFile('./files/11.text', 'utf8', function (err, data) {
if (err) {
return console.log('读取失败' + err)
}
console.log(data)
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 2.fs.writeFile()
没有该文件就创建,但是不能创建目录
写入会覆盖原文件
// options 默认值utf8
fs.writeFile(path,data[,options],callback)
2
// 示例 写入失败 err为错误对象,写入成功 err=null
fs.writeFile('./files/11.text', 'hello', function (err) {
if (err) {
return console.log('写入失败' + err)
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
# 3.文件路径问题
# (1)__dirname
表示当前 js 的目录
console.log(__dirname)
fs.readFile(__dirname + '/files/1.txt', 'uft8', function (err, data) {
console.log(err)
console.log(data)
})
2
3
4
# (2)path 模块
const path = require('path')
path.join() // 将多个路径片段拼接
path.basename(path[,ext]) // 从路径字符串中取出文件名
path.extname(path) // 从路径字符串中取出文件扩展名
2
3
4
// 演示
const pathStr = path.join('/a', '/b/c', '../', '/d', '/e')
console.log(pathStr) // \a\b\d\e
const pathStr2 = path.join(__dirname, './files/1.txt')
const fpath = '/a/b/c/index.html'
var fullName = path.basename(fpath) // index.html
var fullName2 = path.basename(fpath, '.html') // index.html
var fext = path.extname(fpath) // .html
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 二、http 模块
const http = require('http')
# 1.http.createServer()
创建 web 服务器实例
const server = http.createServer()
# 2.server.on()
为服务器实例绑定 request 事件,监听客户端发送的请求
server.on('request', (req, res) => {
console.log(req.url) // 客户端请求地址
console.log(req.method) // 客户端请求方法
// 防止中文乱码,设置响应头
res.setHeader('Content-type', 'text/html; charset=utf-8')
res.end('Hello World') // 给客户端发送指定内容并结束这次请求
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 3.server.listen()
启动 web 服务器监听端口
80 端口可省略 http://127.0.0.1
server.listen(80, () => {})
# 4.简单路由演示
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer()
server.on('request', (req, res) => {
// 获取请求的 url 地址
const url = req.url
// 设置默认响应内容
let content = '<h1>404 Not found!<h1>'
// 判定路径设置返回内容
if (url === '/' || url === '/index.html') {
content = '<h1>首页</h1>'
} else if (url === '/about.html') {
content = '<h1>关于页面</h1>'
}
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html; charset=utf-8')
res.end(content)
})
server.listen(80, () => {
console.log('服务器启动:' + 'http://127.0.0.1')
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 三、模块化
# 1.加载模块
// 加载内置模块
const fs = require('fs')
// 加载用户的自定义模块
const custom = require('./custom.js')
// 加载第三方模块
const moment = require('moment')
2
3
4
5
6
# 2.模块作用域
导入模块时,里面的变量及函数只能有该模块 js 能访问。好处:防止变量污染
而在 html 中,导入 js 后能访问变量和函数,这样会导致多个 js 的变量重复,会被覆盖
// test.js
const name = 'lhd'
function sayHello() {
console.log('Hello World ', name)
}
2
3
4
5
// index.js
const custom = require('./test')
console.log(custom) // 输出:{} 访问不了里面的变量和函数
2
3
# 3.向外共享模块作用域中的成员
简称暴露
# (1)module 对象
每个 .js 自定义模块中都有一个 module 对象,导入模块时,其实是导入 module.exports 指向的对象。默认值为 {}
# (2)module.exports
在 module.exports 对象上挂载属性方法
// test.js
module.exports.name = 'lhd'
module.exports.sayHello = function () {
console.log('Hello World ')
}
2
3
4
5
// index.js
const custom = require('./test')
console.log(custom) // {name:lhd,sayHello:[Function]}
2
3
# (3)exports
简化 module.exports。默认情况下 exports 和 module.exports 指向同一个对象。最终结果以 module.exports 指向的对象为准
// test.js
exports.name = 'lhd'
exports.sayHello = function () {
console.log('Hello World ')
}
2
3
4
5
// index.js
const custom = require('./test')
console.log(custom) // {name:lhd,sayHello:[Function]}
2
3
# (4)同时使用注意事项
使用 require() 模块时,得到的永远是 module.exports 指向的对象
建议只用一种方式,以防混淆

# (5)CommonJS 规范
- 每个模块内部,module 变量代表当前模块。
- module 变量是一个对像,它的 exports 属性(即 module.exports)是对外的接口。
- 加载某个模块,其实是加载该模块的 module.exports 属性。require(0 方法用于加载模块。
# 四、npm 与 包
# 1.什么是包
Node.js 中第三方模块又叫做 包。
# 2.包共享平台
包是由第三方个人或团队开发出来,免费开源
# 3.安装包
在包共享平台中,每个包都有会使用说明
# 默认安装最新
npm install 包名称
npm i 包名称
# 安装多个
npm i 包名称 包名称
# 指定安装版本
npm install 包名称@x.xx.x // x.xx.x为版本
# 第一个x代表大版本,第二个代表功能版本,第三个代表 Bug 修复版本
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 4.切换下包镜像源
下载包速度慢,可以使用镜像服务器
# 查看当前的下包镜像源
npm config get registry
# 将下包的镜像源切换为淘宝镜像源
npm config set registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org/
# 检查
npm config get registry
2
3
4
5
6
# 5.nrm
为了更方便的切换下包的镜像源,我们可以安装 nrm,可快速查看和切换镜像源
# 通过 npm 包管理器,将 nrm 安装为全局可用的工具
npm i nrm -g
# 查看所有可用的镜像源 *号代表目前使用的镜像源
nrm ls
# 将下包镜像源切换为淘宝镜像
nrm use taobao
2
3
4
5
6
# 6.安装完包
初次装包完成后,在项目文件夹下多一个叫做 node modules 的文件夹和 package-lock.json 的配置文件。不要手动修改里面的东西,npm 包管理工具会自动维护。
node modules 文件夹用来存放所有已安装到项目中的包。require() 导入第三方包时,就是从这个目录中查找并加载包。
package-lock.json 配置文件用来记录 node modules 目录下的晦一个包的下载信息,例如包的名字、版本号、下载地址等。
# 7.dependencies
作用:在 package.json 中记录核心依赖包信息
正常安装默认为核心依赖包
# 8.devDependencies
作用:在 package.json 中记录开发依赖包信息
如果某些包只在项目开发阶段用到,在项目上线以后不会用到,建议把这些包记录在 devDependencies 中。相反,如果在开发及上线都用到,则记录在 dependencies 中。一般来说依据官方使用说明安装即可
# 安装到 devDependencies
npm i 包名称 -D
npm install 包名称 --save-dev
2
3
# 9.共享代码
由于第三方包(node_modules)体积过大,不方便分享代码,所以共享时应剔除 node_modules
项目根目录下创建 package.json ,记录安装了哪些包。使用 git 时应把 node_modules 添加到 .gitignore 中。
# 编写代码前先创建 package.json 项目目录不能有中文和空格
# 安装包时,会自动记录包信息到 package.json
npm init -y
# 一次性安装所有的包
npm install
npm i
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 10.卸载包
# 会自动处理 package.json
npm uninstall 包名称
npm uni 包名称
2
3
# 11.模块加载机制
模块在第一次加载后会被缓存。这也意味着多次调用 require0 不会导致模块的代码被执行多次。 注意:不论是内置模块、用户自定义模块、还是第三方模块,它们都会优先从缓存中加载,从而提高模块的加载效率。
- 内置模块加载优先级最高。
- 加载自定义模块时,应指定 ./ 或者 ../ 开头的路径,如果没有将被认为内置模块或者第三方模块。
- 如果加载自定义模块时省略扩展名,则会以
.js、.json、.node进行尝试加载,如果没有则加载失败。 - 加载第三方模块时,会先从父级目录寻找
node_modules,如果父级没有则依次往上寻找。 - 把目录当作模块标识符加载时,会在被加载的目录下查找
package.json并寻找 main 属性,作为加载的入口。如果没有或者无法解析,则会加载目录下的 index.js 文件。
# 五、Express
Web 开发框架。封装 http 内置模块的第三方包
# 1.安装
npm i express
npm i express@4.17.1
2
# 2.创建基本的 Web 服务器
// 导入express
const express = require('express')
// 创建 web 服务器
const app = express()
// 调用 app.listen
app.listen(80, () => {
console.log('express server running at http://127.0.0.1')
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 3.监听 GET 请求
// req:请求对象(包含了与请求相关的属性和方法)
// res:响应对象(包含了与响应相关的属性和方法)
app.get('请求url', function (req, res) {
// 处理函数
})
2
3
4
5
# 4.监听 POST 请求
// req:请求对象(包含了与请求相关的属性和方法)
// res:响应对象(包含了与响应相关的属性和方法)
app.post('请求url', function (req, res) {
// 处理函数
})
2
3
4
5
# 5.把内容响应给客户端
res.send()
app.get('/user', (req, res) => {
res.send({ name: 'lhd', age: '19' })
})
2
3
# 6.获取 URL 中携带的查询参数
req.query
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
console.log(req.query)
})
2
3
# 7.获取 URL 中的动态参数
通过 req.params 对象,可以访问到 URL 中,通过 : 匹配到的动态参数
// 访问 http://127.0.0.1/user/1874
app.get('/user/:id', (req, res) => {
res.send(req.params) // 返回 {id:'1874'}
})
// 访问 http://127.0.0.1/user/1874/lhd
app.get('/user/:id/:name', (req, res) => {
res.send(req.params) // 返回 {id:'1874',name:'lhd'}
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 8.托管静态资源
通过 express.static() 创建静态资源服务器。可将图片、css 文件、js 文件对外开放访问。
// 将 public 目录下资源提供访问。多个目录请多次调用
// 访问地址:http://localhost:端口号/xxx.html
app.use(express.static('./public'))
// 挂载路径前缀
// 访问地址:http://localhost:端口号/public/xxx.html
app.use('/public', express.static('./public'))
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 9.nodemon
类似热更新的工具
编写调试 Node.js 项目时,如果修改了代码则需要重新启动项目才可以使用,使用 nodemon 工具修改代码时可以自动帮我们重启项目,方便开发
# (1)安装
// 安装为全局可用工具
npm i nodemon -g
2
# (2)使用
// 原本启动
node app.js
// nodemon 启动
nodemon app.js
2
3
4
# 六、Express 路由
在 Express 中,路由指的是客户端的请求与服务器处理函数之间的映射关系。 Express 中的路由分 3 部分组成,分别是请求的类型、请求的 URL 地址、处理函数。
// METHOD:请求方式,PATH:请求路径,HANDLER:处理函数
app.METHOD(PATH, HANDLER)
2
# 1.普通路由
挂载到 app 上
// 示例:使用 get 请求返回 get,使用 post 返回 post
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('This is GET request')
})
app.post('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('This is POST request')
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 2.模块化路由
为了方便对路由进行模块化管理,Express 不建议将路由直接挂载到 app 上,而是推荐将路由抽离为单独的模块。
步骤:
- 创建路由模块对应的
.js文件 - 调用 express.Router() 创建路由对象
- 向路由对象上挂载具体的路由
- 使用 module.exports 向外共享路由对象
- 使用 app.use() 注册路由模块
演示:
// ./router/user.js
var express = require('express') // 导入express
var router = express.Router() // 创建路由对象
// 挂载具体路由
router.get('/user/list', (req, res) => {
res.send('Get user list')
})
router.post('/user/add', (req, res) => {
res.send('Add new user')
})
module.exports = router // 向外导出路由对象
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// ./app.js
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const userRouter = require('./router/user.js') // 导入路由模块
app.use(userRouter) // 注册路由模块
app.listen(80, () => {
console.log('http://127.0.0.1')
})
// 访问地址: http://127.0.0.1/user/list
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
为路由模块添加前缀
// 访问地址: http://127.0.0.1/api/user/list
app.use('/api', userRouter)
2
# 七、Express 中间件
请求到达 Express 服务器之后,可连续调用多个中间件,从而对这次请求进行预处理。
和 vue 的路由守卫一样,next()代表放行
# 1.过程

# 2.中间件格式
本质上就是一个 function 处理函数,格式如下:

# 3.next() 函数
next() 函数是实现多个中间件连续调用的关键,它表示把流转关系转交给下一个中间件或者路由。

# 4.定义中间件函数
// mw 指向的就是一个中间件函数
const mw = function(req.res,next){
console.log('这是个简单的中间件函数')
next()
}
2
3
4
5
# 5.全局生效的中间件
只要有请求到达服务器,必先经过 mw 中间件函数处理。相对于 vue 前置守卫,拦截器
// mw 指向的就是一个中间件函数
const mw = function(req.res,next){
console.log('这是个简单的中间件函数')
next()
}
// 全局生效的中间件
app.use(mw)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
简化
app.use(function (req, res, next) {
console.log('这是给简单的中间件函数')
next()
})
2
3
4
# 6.中间件作用
多个中间件之间,共享同一份 req 和 res。基于这样的特性,我们可以在上游的中间件中,统一为 req 或 res 对象添加自定义的属性或方法,供下游的中间件或路由进行使用。
// 示例:每个请求都需要获取时间
app.use((req, res, next) => {
req.startTime = Date.now()
next()
})
app.get('/user', (req, res) => {
res.send('time:' + req.startTime)
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 7.多个中间件
按注册顺序排,且必须在路由上方。多个中间件共享 req 和 res。
// 完整示例
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('第一个中间件')
next()
})
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('第二个中间件')
next()
})
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send({ info: '请求了服务器', method: req.method })
})
app.listen(80, () => {
console.log('http://127.0.0.1')
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 8.局部生效的中间件
const mw = function (req, res, next) {
console.log('中间件函数')
next()
}
app.get('/', mw, (req, res) => {
res.send('Hellow World')
})
app.get('/user', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hellow World')
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 9.多个局部中间件
// mw1与mw2 为中间件函数,两种方式等价
app.get('/', mw1, mw2, (req, res) => {
xxx
})
app.get('/', [mw1, mw2], (req, res) => {
xxx
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 10.中间件的分类
# (1)应用级别的中间件
通过 app.use() 或者 app.get() 或 app.post() ,绑定到 app 实例上的中间件。
# (2)路由级别的中间件
绑定到 express.Router() 实例上的中间件。
用法与应用级别中间件一致。
var app = express()
var router = express.Router()
router.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('路由级别中间件')
next()
})
app.use('/', router)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# (3)错误级别的中间件
专门用来捕获项目中发生的异常错误,从而防止项目崩溃。
格式:处理函数中必须有 4 个形参 (err,req,res,next)
特点:必须注册在所有路由之后
// 示例
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
throw new Error('服务器出错') // 错误发生后,下面的语句无法执行
res.send('Hellow World') // 无法响应
})
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
console.log('发生了错误' + err.message)
res.send('Error!' + err.message) // 捕获错误,向客户端响应
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# (4)Express 内置中间件
express@4.16.0版本开始,内置了 3 个常用的中间件
express.static 快速托管静态资源的内置中间件 (无兼容性)
express.json 解析 JSON 格式的请求体数据 (仅在 4.16.0 +可用)
express.urlencoded 解析 URL-encoded 格式的请求体 (仅在 4.16.0 +可用)
// 配置解析 application/json 格式数据的内置中间件
app.use(express.json())
// 配置解析 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 格式数据的内置中间件
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }))
2
3
4
演示:
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
// 注意:除了错误级别的中间件,其他的中间件,必须在路由之前进行配置
// 通过express.json()这个中间件,解析表单中的JSON格式的数据
app.use(express.json())
// 通过express.urlencoded()这个中间件,来解析表单中的url-encoded格式的数据
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }))
app.post('/user', (req, res) => {
// 在服务器,可以使用req.body这个属性,来接收客户端发送过来的请求体数据
// 默认情况下,如果不配置解析表单数据的中间件,则req.body默认等于undefined
console.log(req.body)
res.send('ok')
})
app.post('/book', (req, res) => {
// 在服务器端,可以通过req,body来获取JSON格式的表单数据和url-encoded格式的数据
console.log(req.body)
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# (5)第三方中间件
非官方内置,由第三方开发出来的中间件叫第三方中间件,可用按需加载和配置
例如:在 express@4.16.0 之前的版本中,经常使用 body-parser 这个第三方中间件来解析请求体数据。
使用步骤如下:
- 使用
npm i body-parser安装 - 使用
require导入中间件 - 使用
app.use()注册并使用中间件
演示:
const parser = require('body-parser')
app.use(parser.urlencoded({ extended: false }))
2
# 11.自定义中间件
自定义一个解析请求体数据的中间件并使用
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
// 自定义中间件函数,解析请求体数据
const parserBody = function (req, res, next) {
let str = ''
// 请求数据过大时,data会分段发送,所以用on绑定data事件,监听data返回的数据并组装
req.on('data', (chunk) => {
str += chunk
})
// 当数据发送完毕后,会触发end事件,所以在end处将数据挂载为body传给路由
req.on('end', () => {
req.body = str
next()
})
}
// 注册全局中间件
app.use(parserBody)
app.post('/', (req, res) => {
// 在此可以拿到挂载的数据并返回数据
res.send('返回的数据:', req.body)
})
app.listen(80, () => {
console.log('http://127.0.0.1')
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
测试结果:

# 12.封装自定义中间件
// test.js
function test(req, res, next) {
/*中间件处理函数*/
}
module.exports = test // 暴露出去
// app.js
const test = require('./test') // 导入自定义中间件
app.use(test) // 注册
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 八、CORS 中间件
# 1. 基本使用
安装
npm i cors
使用
// app.js
const cors = require('cors') // 导入
app.use(cors()) // 配置中间件,需在路由之前
2
3
# 2. CORS 响应头部
# (1)Access-Control-Allow-Origin
响应头部可以携带一个 Access-Control-Allow-Origin 字段,语法如下
// origin 参数的值指定了只允许访问该资源的外域 url
Access-Control-Allow-Origin:<origin>|*
2
示例:
// 只允许来自 http://127.0.0.1 的请求
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', 'http://127.0.0.1')
2
// 允许任何域的请求
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*')
2
# (2)Access-Control-Allow-Headers
默认情况下,CORS 仅支持客户端向服务器发送如下 9 个请求头:
Accept、Accept-Language、Content-Language、DPR、Downlink、Sava-Data、Viewport-width、Width、Content-Type(值仅限于 text/plain、multipart/form-data、application/x-www-form-urlencoded 三者之一)
如果客户端向服务器发送额外的请求头信息,则需要在服务器端,通过 Access-Control-Allow-Headers 对额外请求头进行声明,否则请求失败。
示例:
// 允许客户端额外向服务器发送Content-Type请求头和X-Custom-Header请求头
// 注意:多个请求头之间使用英文的逗号进行分割
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'Content-Type,X-Custom-Header')
2
3
# (3)Access-Control-Allow-Methods
默认情况下,CORS 仅支持客户端发起 GET、POST、HEAD 请求。
如果客户端希望通过 PUT、DELETE 等方式请求服务器的资源,则需要在服务器端,通过Access-Control-Alow-Methods 来指明实际请求所允许使用的 HTTP 方法。
示例:
// 只允许POST、GET、DELETE、HEAD请求方法
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'POST,GET,DELETE,HEAD')
// 允许所有的HTTP请求方法
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', '*')
2
3
4
# 3.CORS 请求分类
# (1)简单请求
同时满足以下两大条件的请求,就属于简单请求:
- 请求方式:GET、POST、HEAD 三者之一
- HTTP 头部信急不超过以下几种字段:无自定义头部字段、Accept、Accept-Language、Content-Language、DPR、Downlink、Save-Data、Viewport-Width、Width、Content-Type(只有三个值 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 、multipart/form-data、text/plain)
# (2)预检请求
只要符合以下任何一个条件的请求,都需要进行预检请求:
- 请求方式为 GET、POST、HEAD 之外的请求 Method 类型
- 请求头中包含自定义头部字段
- 向服务器发送了 application./json 格式的数据
在浏览器与服务器正式通信之前,浏览器会先发送 OPTION 请求进行预检,以获知服务器是香允许该实际请求,所以这一次的 OPTION 请求称为“预检请求”。服务器成功响应预检请求后,才会发送真正的情求,并且携带真实数据。
# (3)简单请求与预检请求区别
简单请求的特点:客户端与服务器之间只会发生一次请求。 预检请求的特点:客户端与服务器之间会发生两次请求,OPTION 预检请求成功之后,才会发起真正的请求。
# 九、JSONP
概念:浏览器端通过 <script> 标签的 src 属性,请求服务器上的数据,同时,服务器返回一个函数的调用。这种请求数据的方式叫做 JSONP。
特点:
- JSONP 不属于真正的 Ajax 请求,因为它没有使用
XMLHttpRequest这个对象, - JSONP 仅支持 GET 请求,不支持 POST、PUT、DELETE 等请求。
# 1.实现 JSONP 接口
步骤:
- 获取客户端发送过来的回调函数的名字
- 得到要通过 JSONP 形式发送给客户端的数据
- 根据前两步得到的数据,拼接出一个函数调用的字符串
- 把上一步拼接得到的字符串,响应给客户端的
<script>标签进行解析执行
演示:
// 服务器端
app.get('/api/jsonp',(req,res)=>
//1.获取客户端发送过来的回调函数的名字
const funcName req.query.callback
/2.得到要通过JSONP形式发送给客户端的数据
const data = { name:'lhd',age:19 }
//3.根据前两步得到的数据,拼州接出一个函数调用的字符串
// xxx = `$(funcName)(${JSON.stringify(data)})` md文档不识别``
const scriptstr = xxx
//4.把上步拼接得到的字符串,响应给客户端的<scr1pt>标签进行解析执行
res.send(scriptstr)
})
// 客户端
$.ajax({
method:'GET',
url:'http://127.0.0.1/api/jsonp',
dataType:'jsonp', //表示要发起J50NP的i情球
success:function (res){
console.log(res)
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 十、MySQL
安装模块
npm i mysql -y
# 1.基本使用
// 1.导入 MySQL 模块
const mysql require('mysql')
// 2.建立与 MySQL 数据车的连接
const db = mysql.createPool({
host:'127.0.0.1:3306', // 数据库的IP地址
user:'root', // 登录数据库的账号
password:'123456', // 登录数据的密码
database:'my_db_01' // 指定要操作哪个数据库
// port:'3306' 默认为3306,所以可以不写
})
// 检查 MySQL 模块能香正常工作
db.query('SELECT 1',(err,results)=>
if (err)return console.log(err.message)
// 只要能打印出【RowDataPacket{'1':1}】的结果,就证明数据库连接正常
console.log(results)
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 2.查询数据
const strSql = 'select * from test' // test是我的数据库表
db.query(strSql, (err, results) => {
if (err) console.log(err)
console.log(results)
})
2
3
4
5
# 3.插入数据
const strSql = 'insert into test(name) value (?) ' // test是我的数据库表 ?代表占位符
const user = { name: 'ddd' } // name是我的数据库字段
db.query(strSql, [user.name], (err, results) => {
if (err) console.log(err)
console.log(results)
})
2
3
4
5
6
# 4.简单封装
我以自己的思路封装一下
// mysql.js 封装的插入函数
const mysql = require('mysql')
// 连接数据库
const db = mysql.createPool({
host: '127.0.0.1',
user: 'root',
password: '',
database: 'bookshop',
})
// 向test表插入name
function add(data) {
let strSql = 'insert into test (name) value (?)'
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
db.query(strSql, [data], async (err, results) => {
if (err) reject(err.message)
resolve(results)
})
})
}
module.exports = add
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
// app.js
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const add = require('./mysql')
// 解析 json 数据
app.use(express.json())
app.post('/', (req, res) => {
add(req.body.name)
.then(() => {
res.send({ code: '', message: '插入成功' })
})
.catch(() => {
res.send({ code: '1001', message: '插入失败' })
})
})
// 捕捉异常中间件
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
console.log('发生了错误!' + err.message)
res.send('Error!' + err.message) // 捕获错误,向客户端响应
})
app.listen(80, () => {
console.log('http://127.0.0.1')
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27


# 十一、前后端身份认证
# 1. Session
中间件,配合 cookie 使用,默认不支持跨域
# (1)安装
npm i express-session
# (2)使用
var session = require('express-session')
app.use(
session({
secret: 'keyboard cat', // secret值可为任意字符串
resave: false,
saveUninitialized: true,
})
)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# (3)存储 session 数据
app.post('/api/login', (req, res) => {
//判断用户提交的登录信息是否正确
if (req.body.username !== 'admin' || req.body.password !== '000000') {
return res.send({ status: 1, msg: '登录失败' })
}
req.session.user = req.body
//将用户的信息,存储到Session中
req.session.islogin = true
//将用户的登录状态,存储到Session中
res.send({ status: 0, msg: '登录成功' })
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# (4)读取 session 数据
//获取用户姓名的接口
app.get('/api/username',(req,res)=>{
//判断用户是否登录
if (!req.session.islogin){
return res.send({status:1,msg:'fail'})
}
res.send({status:0,msg:'success',username:req.session.user.username }
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# (5)清空 session 数据
//退出登录的接口
app.post('/api/logout',(req,res)=>
//清空当前客户端对应的session信息
req.session.destroy()
res.send({
status:0,
msg:'退出登录成功'
})
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 2. JWT
JSON Web Token ,支持跨域认证 , 通常由三部分组成 :header (头部)、Playload (有效荷载,加密信息)、Signature(签名)。由 . 分割
Header.Playload.Signature
# (1)安装
# jsonwebtoken 用于生成 JWT 字符串
# express-jwt 用于将 JWT 字符串解析还原成JSON对像
npm i jsonwebtoken express-jwt
2
3
# (2)导入
//1,导入用于生成 JWT 字符串的包
const createJWT = require('jsonwebtoken')
//2.导入用于将客户端发送过来的 JWT 字符串,解析还原成JSON对象的包
var { expressjwt: jwt } = require('express-jwt')
2
3
4
# (3)定义 Secret 密钥
为了保证 JWT 字符串的安全性,防止 JWT 字符串在网络传输过程中被别人破解,我们需要专门定义一个用于加密和解密的 secret 密钥:
- 当生成 JWT 字符串的时候,需要使用 secret 密钥对用户的信息进行加密,最终得到加密好的 JWT 字符串
- 当把 JWT 字符串解析还原成 JSON 对象的时候,需要使用 secret 密钥进行解密
// 密钥为字符串
const secretKey = 'dddhl ^_^'
2
# (4)登录后生成 JWT 字符串
// 登录接口
app.post('/api/login', function (req, res) {
// 省略登录失败情况下的代码
// 用户登录成功之后,生成WT字符串,通过token属性响应给客户端
res.send({
status: 200,
message: '登录成功',
// 调用 jwt.sign() 生成 JWT 字符串,三个参数分别是:用户信息对象、加座密钥、配置对象
// 2h 代表token有效期2小时,s为秒
token: createJWT.sign({ username: 'lhd' }, secretKey, { expiresIn: '2h' }),
})
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# (5)将 JWT 解析还原成 JSON 对象
请求时,请在 Authorization 字段将 token 发送到服务器
// 使用app.use()来注册中间件
// .unless({ path: [/^\/api\//] })用来指定哪些接口不需要访问权限 这里表示的是 api开头的接口都不需要token
app.use(
jwt({
secret: secretKey,
algorithms: ['HS256'],
}).unless({ path: [/^\/api\//] })
)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# (6)获取解析还原的 JSON 对象
解析完成后,req.auth = 解析出来的对象
app.get('/admin/getinfo',(req,res)=>{
console.log(req.auth)
res.send({
status:200,
message:'获取用户信息成功l
data:req.auth
})
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# (7)处理 token 过期
app.use(function (err, req, res, next) {
if (err.name === 'UnauthorizedError') {
return res.send({ status: 401, message: '登录信息已过期' })
}
return res.send({ status: 400, message: '其他错误' })
})
2
3
4
5
6
# (8)完整演示
请求登录时发送 username ,不用 token。
服务端生成 token 返回给客户端。
客户端请求解析 token 接口,需要 token。
注意:请求 token 接口时,Header 里需要 Authorization: 'Bearer ' + token 注意 Bearer 后面有个空格隔开 token
const express = require('express')
const createJWT = require('jsonwebtoken')
var { expressjwt: jwt } = require('express-jwt')
const app = express()
// token密钥
const secretKey = 'dddhl ^_^'
// json解析
app.use(express.json())
// token解析
app.use(
jwt({
secret: secretKey,
algorithms: ['HS256'],
}).unless({ path: [/^\/api\//] })
)
// 登录接口,自动生成token,接收一个username存进token
app.post('/api/login', (req, res) => {
let token = createJWT.sign({ username: req.body.username }, secretKey, {
expiresIn: '30s',
})
res.send({
status: 200,
message: '登录成功',
token: token,
})
})
// 测试token解析,发送解析后的数据,请求时需要token
app.get('/token', (req, res) => {
console.log(req.auth)
res.send({
status: '200',
message: '检测token解析成功',
data: req.auth,
})
})
// 处理token过期
app.use(function (err, req, res, next) {
if (err.name === 'UnauthorizedError') {
return res.send({ status: 401, message: '登录信息已过期' })
}
return res.send({ status: 400, message: '其他错误' })
})
app.listen(80, () => {
console.log('http://127.0.0.1')
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
登录后生成 token:

获取解析后的 token 数据:


v1.4.16